Which of the Following Best Describes Graft Versus Host Disease
06 2020 GLOBE NEWSWIRE -- The Graft-Versus-Host Disease. Graft-versus-host GVH disease can occur when _____.

Chronic Graft Versus Host Disease Gvhd In Children Semantic Scholar
Graft-versus-host disease GVHD is a major complication following allogeneic HSCT which significantly affects non-relapse mortality.

. In GvHD the donated bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cells view the recipients body as foreign and the donated cellsbone marrow attack the body. High-dose chemotherapy radiotherapy inflicts cellular damage and this leads to an inflammatory process. Although the main cause of death in patients who have undergone HSCT is from relapse of the primary disease a sizeable number of these patients die from infections related to graft-versus-host disease GVHD second malignancies or cardiac or pulmonary issues2-5 In addition other studies have revealed that up to 40 of HSCT survivors experience severe.
What are the similarities between graft versus host disease and graft rejection. 06 2020 -- The Graft-Versus-Host Disease. Which of the following best describes graft-versus-host disease.
Acute graft-versus-host disease aGvHD occurs following an allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplant and is a reaction of donor immune cells against host tissues and remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality Greinix 2008. Submit 1 document per part. White blood cells of the donors immune system which remain within the donated tissue the graft recognize the recipient the host as foreign non-self.
Graft-versus-host disease GvHD is a complication that can occur after certain stem cell or bone marrow transplants in which the transplanted cells attack the recipients body. Which of the following does NOT constitute an advantage of using 2. Minimum three paragraphs per page.
Graft-versus-host disease GvHD is a syndrome characterized by inflammation in different organsGvHD is commonly associated with bone marrow transplants and stem cell transplants. Cutaneous manifestations are the earliest and most common presentation of the disease. A tissue transplant is rejected because the hosts T cytotoxic cells are activated and kill the transplanted tissue.
7MM Epidemiology Forecast to 2028. Chronic graft versus host disease cGvHD. The graft MUST contain immunocompetent alloreactive T cells.
Graft-versus-host disease GVHD is an adverse immunologic phenomenon following allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplant. There are two types of GvHD. And ocular manifestations of.
Immune cells attack transplanted tissue in a privileged site. Which of the following types of transplant is least compatible. Epidemiology Forecast to 2028 report has been added.
Immune cells in transplanted bone marrow attack the cells of the host. Graft versus host disease GVHD is an immune-mediated condition resulting from a complex interaction between donor and recipient adaptive immunity. Basiliximab is an immunosuppressive monoclonal antibody used for rejection prevention following solid organ transplantation.
The Global Graft Versus Host Disease Treatment Market size was estimated at USD 142178 million in 2020 and expected to reach USD 155728 million in 2021 at a CAGR of 996 to reach USD 2764. We describe our single-center experience with 6 cases of GVHD diagnosed over a period of 14 years in a total of 604 liver transplant recipients--283 deceased donor liver transplants DDLT and 321 living-related liver transplants LDLT. The white blood cells present.
Graft versus host disease GVHD is a rare complication following liver transplantation LT and has high mortality. The pharmacokinetics PK of basiliximab in this setting are known. Acute GvHD occurs usually within the first six months after a transplant whereas chronic GvHD occurs usually more.
Graft versus host disease GvHD is a condition that might occur after an allogeneic transplant. The donor cells are called the graft and the patient is called the host. The recipient MUST be incapable of.
Graft-versus-host disease GvHD was first described in 1959 since then major efforts have been made in order to understand its physiopathology and animal models have played a key role. T and B cells are transplanted Following an organ transplant therapeutic immunosuppression to prevent organ rejection may be accomplished by any of the following EXCEPT __________. Which of the following best describes graft-versus-host disease.
The graft MUST be capable of recognizing foreign Ag on host tissue. There are two forms of GvHD. 1 Acute GVHD describes a distinctive syndrome of dermatitis see the image below hepatitis and enteritis developing within 100 days after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation HCT.
Basiliximab may also be used for prophylaxis and treatment of graft-versus-host disease GVHD in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell. 1 Minimum 6 full pages No word count per page- Follow the 3 x 3 rule. Graft-Versus-Host Disease GvHD.
Immune cells in transplanted bone marrow attack the cells of the host. This article describes the pathophysiology clinical presentation diagnosis and treatment options available for acute and chronic GVHD. Acute graft versus host disease aGvHD.
Graft-versus-Host Disease GVHD is a common condition after a bone marrow or stem cell transplant that uses cells from a donor an allogeneic transplant.
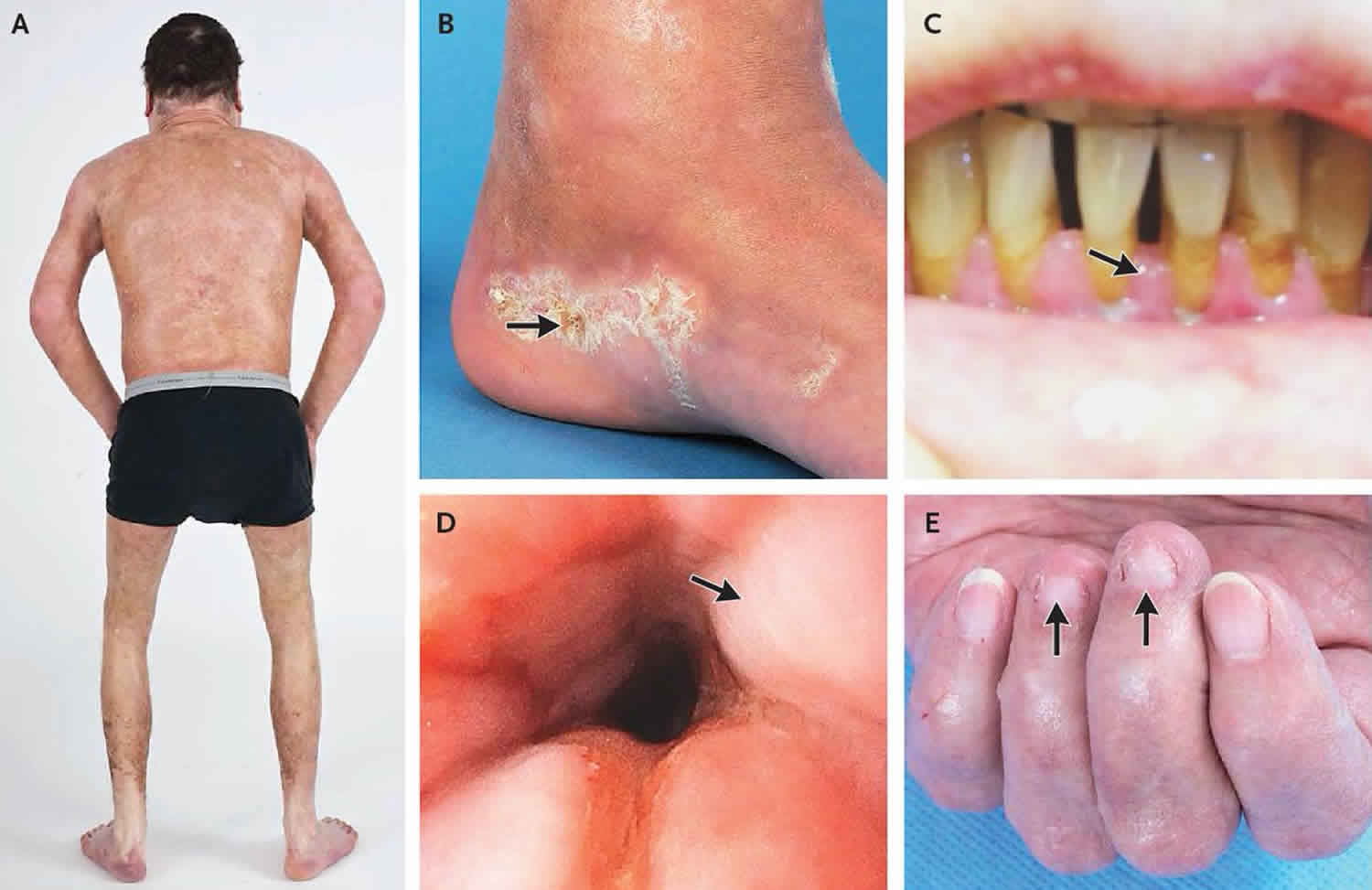
Graft Versus Host Disease Causes Signs Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment

Clinical Pathologic Classifi Cation Of Chronic Graft Versus Host Download Scientific Diagram

No comments for "Which of the Following Best Describes Graft Versus Host Disease"
Post a Comment