Describe the Systemic and Pulmonary Blood Circulation Routes
Click here to view We have moved all content for this concept to for better organization. In the human heart two coronary arteries arise from the aorta just beyond the semilunar valves.

Pulmonary And Systemic Circulations Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation
The main difference between pulmonary and systematic circulation is that pulmonary circulation carries.

. Please update your bookmarks accordingly. The deoxygenated blood shoots down from the right atrium to the right ventricle. This deoxygenated blood then passes to the right.
The right atrium the left ventricle the aortic valve the aortic branches all of the capillaries with the exception of those involved with the exchange of gases and the veins with the exception of the pulmonary veins. Systemic circulation runs to and from the cells in your body. The pulmonary and systemic circulation make up the two 2 major branches of the cardiovascular system and are connected to either side of the heart.
In systemic circulation however blood flows in one direction from left to right. Pulmonary Circulation takes deoxygenated blood and converts it back to oxygenated blood while systemic circulation takes the oxygenated blood to the cells and brings back the deoxygenated blood that is released by the cells in the body. To better organize out content we have unpublished this concept.
Describe systemic and pulmonary circulation. After moving through the pulmonary circuit oxygen-rich blood in the left ventricle leaves the heart via the aorta. The main role of the pulmonary circulation is that it allows.
The cardiovascular system is composed of two circulatory paths. There Are Two Types of Circulation. The systemic circuit is the path of circulation between the heart and the rest of the body excluding the lungs.
1 Answer 1 vote. Answered Oct 25 by Mishika 473k points selected Oct 26 by ShanayaBasu. There the blood drops off oxygen nutrients.
The pulmonary circulation is the transportation of de-oxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for the re-saturation of the blood with oxygen before entering of blood into the systemic circulation. The systemic circuit is the path of circulation between the heart and the rest of the body excluding the lungs. The blood travels from the main artery to larger and smaller arteries and into the capillary network.
Click Create Assignment to assign this modality to your LMS. A separate systemic circulation supplies blood flow to the airways from the carina to the terminal bronchioles. The following phase is called the ejection period which is when both ventricles pump the blood into the large arteries.
Pulmonary circulation the circuit through the lungs where blood is oxygenated and systemic cir. This blood is circulated from the aorta to the rest of the body by various major and minor arteries. The Route of Pulmonary Circulation.
Blood goes to all over the. In addition bronchial arteries provide nutritive flow to the lower trachea airway nerves and lymph nodes. This page should be used as you analyse the movement of blood through.
Pulmonary Circulation and Systemic Circulation Pulmonary circulation moves blood. The blood enters the pulmonary circulation stream from the system circulation stream when the blood with depleted oxygen reserves reaches the right atrium via the inferior and superior venae cavae. Veins return oxygen-depleted blood back.
During diastole the increased aortic pressure above the valves forces blood into the coronary arteries and thence into the musculature of the heart. You have greater circulation or the systemic circulation. In the systemic circulation the left ventricle pumps oxygen-rich blood into the main artery aorta.
Arteries deliver oxygenated blood to tissues. In summary from the video in 14 steps blood flows through the heart in the following order. 1 body 2 inferiorsuperior vena cava 3 right atrium 4 tricuspid valve 5 right ventricle 6 pulmonary arteries 7 lu ngs 8 pulmonary veins 9 left atrium 10 mitral or bicuspid valve 11 left ventricle 12 aortic valve 13 aorta 14 body.
From the right atrium the blood is pumped into hearts right ventricle via the tricuspid valve. The Heart Powers Both Types of Circulation The heart pumps oxygenated blood out of the. The oxygenated blood shoots from the left atrium to the left ventricle below to begin.
Where the Blood Goes The main difference between the two circulatory systems is the destination of the blood thats being circulated. Coronary circulation part of the systemic circulatory system that supplies blood to and provides drainage from the tissues of the heart. Afterwards the blood enters the.
Pulmonary circulation is the system of transportation that shunts de-oxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to be re-saturated with oxygen before being dispersed into the systemic circulation. Once these cycles are complete deoxygenated blood is returned to your heart via pulmonary veins. We have a new and improved read on this topic.
2223 The drainage of bronchial vessels into the pulmonary circulation and the large veins has a complex arrangement eFig. Heart contracts repeatedly each time it pumps its supply of deoxygenated blood through pulmonary circulation. The systemic routes of circulation include every part of the bodys circulatory system which are uninvolved in the pulmonary routes of circulation.
Pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation go hand in hand and are jointly responsible for sending blood throughout the body. The main difference between pulmonary and systematic circulation is that pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs and oxygenated blood back to the heart whereas systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the heart throughout the body and deoxygenated blood back to the heart. In human beings there is double circulation because blood passes twice through the heart during one cardiac cycle.
The pulmonary circulation system is the only pathway through which the complete cardiac output passes. Share It On Facebook Twitter Email. The systemic circulatory system circulates oxygenated blood from the heart around the body into the tissues before returning deoxygenated blood to the heart.
The blood moves to the lungs exchanges carbon dioxide for oxygen and returns to the left atrium. The heart then pumps it out of the right ventricle and into the pulmonary arteries to begin pulmonary circulation. After moving through the pulmonary circuit oxygen-rich blood in the left ventricle leaves the heart via the aorta.
The cardiovascular division of the circulatory system is further broken into two 2 the pulmonary and systemic circulation. The differences between them are listed below. Describe pulmonary and systemic circulation.
This page will be removed in. Describes pulmonary and systemic circulations. Deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body enters the heart from the inferior vena cava while deoxygenated blood from the upper body is delivered to the heart.
Pulmonary circulation carries blood to and from the oxygen-exchange surfaces within a persons lungs. The Routes and Function of Blood Flow 1. Goes to lungs in this system from the right side of heart.
In pulmonary circulation the right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the superior vena cava which drains blood from the veins of the upper organs and arms. Key Areas Covered 1. Pulmonary Circulation and Systemic Circulation.

What Is The Path Of Blood Through The Circulatory System
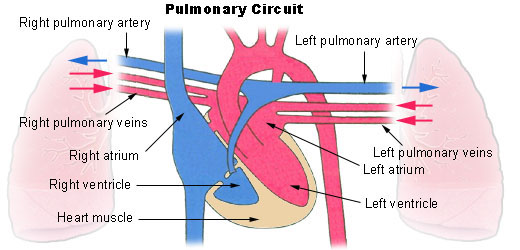
Seer Training Circulatory Pathways

Bio121 Systemic And Pulmonary Circulations Flashcards Quizlet
No comments for "Describe the Systemic and Pulmonary Blood Circulation Routes"
Post a Comment